Demystifying Cloud Services: Understanding IaaS, SaaS, and PaaS
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, three key service models have emerged, each catering to distinct needs and preferences. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS) represent different layers of cloud computing, providing flexibility, scalability, and varying levels of control to users. Let's delve into each of these cloud service models to unravel their functionalities and benefits.
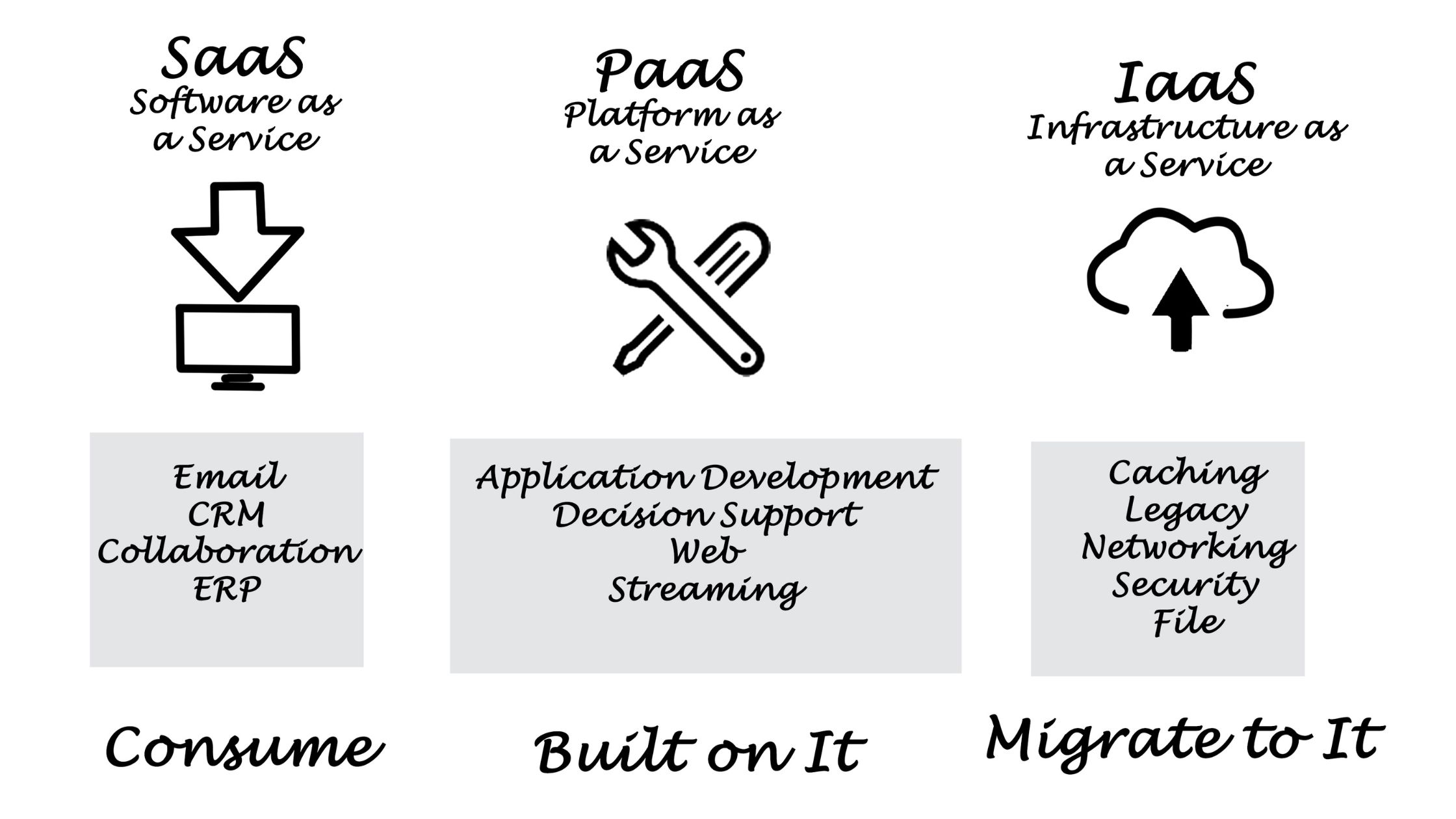
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
IaaS is the foundational layer of cloud computing, offering virtualized computing resources over the internet. In this model, users have control over the fundamental building blocks of computing infrastructure, including virtual machines, storage, and networking. IaaS provides a scalable and flexible solution, enabling users to rent resources on-demand. This is particularly beneficial for businesses that require full control over their operating systems and applications but want to avoid the overhead of managing physical hardware. Popular IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Key Features of IaaS:
- On-demand resources: Users can provision and de-provision computing resources as needed.
- Scalability: IaaS allows for easy scaling of resources based on demand.
- Control: Users have control over the infrastructure, including operating systems and applications.
Software as a Service (SaaS):
SaaS represents a higher layer of abstraction in cloud computing, delivering fully functional applications over the internet. Instead of managing infrastructure or worrying about software updates, users can access and use applications directly through a web browser. SaaS is an ideal solution for businesses looking to streamline their operations without the burden of software maintenance. Popular examples of SaaS include Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Salesforce, and Dropbox.
Key Features of SaaS:
- Accessibility: Applications are accessible from any device with an internet connection and a web browser.
- Maintenance-free: Software updates and maintenance are handled by the service provider.
- Cost-effective: Users pay for subscriptions, eliminating the need for upfront software licensing and ongoing maintenance costs.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
PaaS sits between IaaS and SaaS, offering a platform that allows users to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with the complexities of underlying infrastructure. PaaS provides a framework that includes development tools, databases, and middleware, allowing users to focus solely on building and deploying applications. This model is suitable for developers seeking efficiency in the application development life cycle. Popular PaaS providers include Heroku, Microsoft Azure App Service, and Google App Engine.
Key Features of PaaS:
- Streamlined development: PaaS accelerates the application development process with pre-built tools and services.
- Simplified deployment: Users can deploy applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
- Cost efficiency: PaaS reduces the need for managing infrastructure, leading to cost savings.
Choosing the Right Model:
The selection of the appropriate cloud service model depends on specific business requirements, technical expertise, and desired levels of control. Larger enterprises with complex IT infrastructure needs may prefer the granular control offered by IaaS. Meanwhile, smaller businesses looking for hassle-free software solutions might opt for the simplicity of SaaS. PaaS strikes a balance, providing a platform for developers while abstracting infrastructure concerns.
In conclusion, IaaS, SaaS, and PaaS are integral components of the cloud computing ecosystem, catering to diverse user needs. Understanding the distinctions between these service models empowers businesses to make informed decisions based on their unique requirements, ultimately leveraging the benefits of cloud computing for enhanced flexibility, scalability, and efficiency.
Read Also: PRINCIPLES AND SKILLS THAT DRIVE DEVOPS EXCELLENCE
Read Also: AUTOMATION: EMPOWERING DEVOPS EXCELLENCE